The article provides an in-depth look at what occurs when you delete an email in Outlook, whether others can still see deleted messages, and if they are removed from the server.
Deleting an email in Outlook might seem straightforward, but have you ever wondered where the message goes, if it's truly gone, or whether others can still see it? This article breaks down the process, answers these questions, and explains how email deletion works in Outlook.
What happens when you delete Outlook email?
When you delete a message in Outlook, it doesn't vanish from your mailbox immediately. Instead, it goes through several stages before being permanently removed. Here's what happens step-by-step:
Step 1. Deleted Items folder
When you delete an email in Outlook – whether by hitting the Delete key, using the Ctrl + D shortcut or clicking the trash bin icon – the message is moved to the Deleted Items folder.
This folder acts as a safety net, giving you the chance to recover emails if you've deleted them by mistake. When the Deleted Items folder is emptied, the message is marked for removal, but it is still not completely erased. Instead, it gets to the Recoverable Items folder.
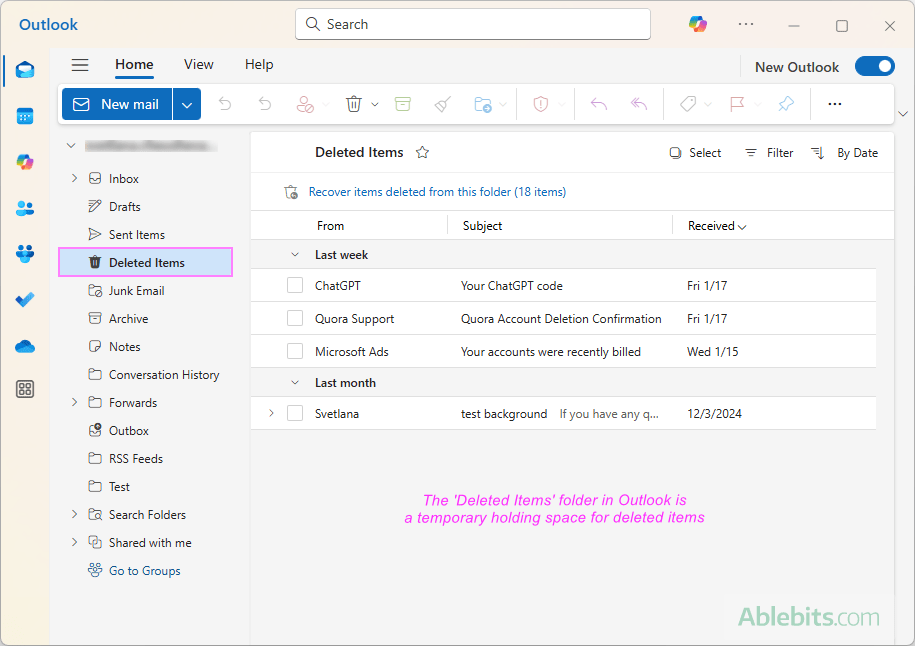
Step 2. Recoverable Items folder
The Recoverable Items folder, which is hidden in Outlook, acts as a second temporary holding space for deleted items, giving you one more chance to restore accidentally deleted messages before they are completely wiped out. Emails stay in the Recoverable Items folder until they are automatically purged by Outlook in accordance with its retention policies or until you delete them manually from this folder.
Emails are moved to the Recoverable Items folder when any of the following actions occur:
- A message is manually deleted from the Deleted Items folder.
- The Deleted Items folder is emptied.
- An item is permanently deleted using the Shift + Delete shortcut.
- When an email is removed from the Deleted Items folder (either manually or automatically), it is moved to Recoverable Items instead of being erased immediately.
- Emails in the Recoverable Items folder remain accessible for a limited time, depending on your Outlook's retention policies.
- The default retention period during which users can restore deleted items is 14 days.
- For corporate or educational accounts, administrators can extend the retention period up to 30 days based on organizational needs.
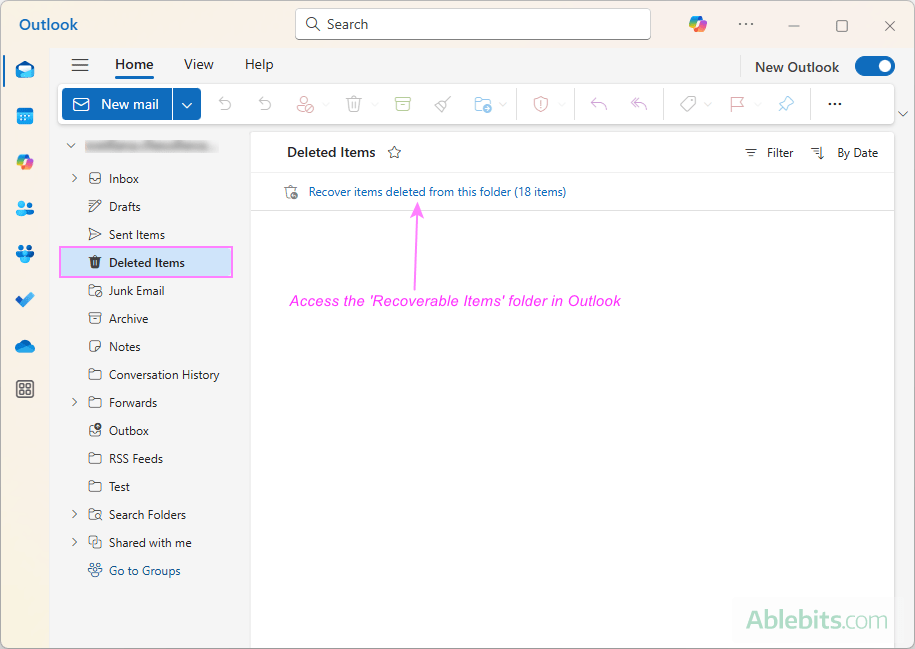
- To restore emails from the Recoverable Items folder, you can use the Restore option.
Here's how it works:
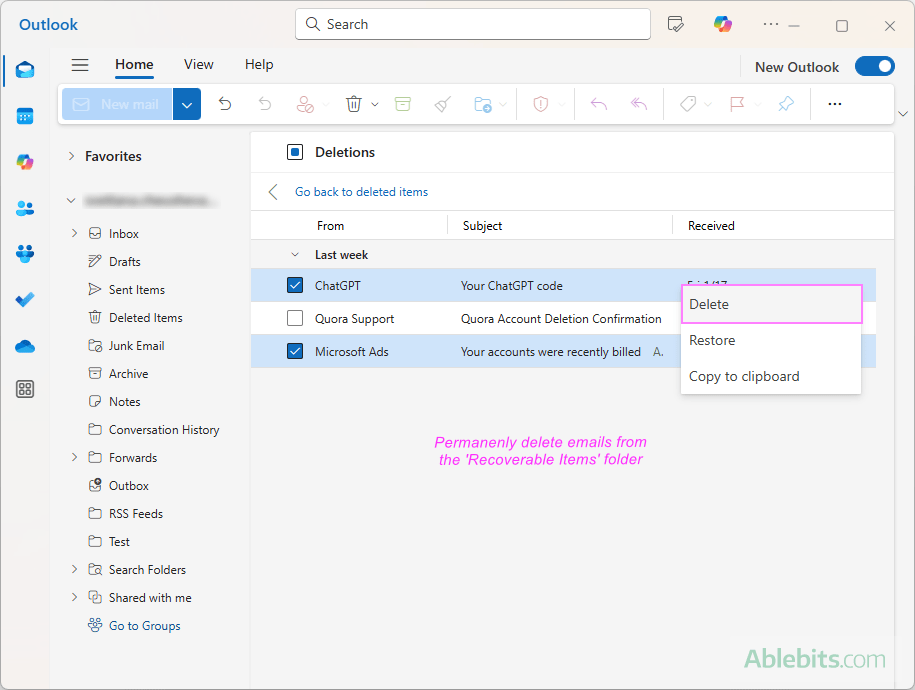
Step 3. Permanent deletion
Once the retention period expires or you manually purge deleted items from the Recoverable Items folder, the emails are permanently deleted. At this stage:
- The emails are removed from Microsoft servers and are no longer recoverable through Outlook.
- In corporate or educational environments, administrators might still be able to retrieve them for a limited time using advanced recovery tools, depending on how the retention and archiving settings are configured.
For more information, see:
Key points to remember
- Deleted emails aren't immediately gone. Messages that you delete in Outlook pass through the Deleted Items and Recoverable Items folders, offering opportunities for recovery.
- Retention policies vary. Personal Outlook accounts default to a 14-day recovery window, while company accounts may have extended timeframes.
- Final deletion is irreversible. Once emails are removed from the Recoverable Items folder, they cannot be recovered through Outlook or Microsoft servers.
Knowing the nuances of what happens after deleting Outlook emails can help you manage your inbox more confidently and recover important messages when it counts, especially in a professional setting.
Can other people still see deleted Outlook email?
Understanding whether others can see a message after you delete it in Outlook requires a basic grasp of how email delivery and storage work. Here are the key points:
- Multiple servers. When you send an email, it passes through multiple servers before reaching the recipient. Each server creates a copy to ensure delivery, even if one server fails.
- Copies in mailboxes. Once delivered, a copy of the email is stored in the recipient's Inbox, while another copy remains in your Sent Items folder.
This distribution means multiple copies of the same email can exist, so others may still see your message after you delete it. Below are the main factors that determine if others can see a deleted email.
An email was only in your mailbox
If you delete a message that exists solely in your Outlook (e.g. in the Drafts folder), no one else can see it unless they have access to your account.
An email was in a shared mailbox
In collaborative environments such as shared mailboxes, deleting an email does not remove it for other users. It will still appear in the Deleted Items folder and the Recoverable Items folder, allowing others to restore it.
Synchronization across devices
When using synchronized accounts like Outlook 365, deleting an email on one device (desktop, mobile, or web) deletes it across all devices. This ensures consistency, but it also means the message is removed everywhere in your account.
A message was sent to someone else
When you delete an email from your Sent Items folder, you're only removing your copy. The email will still exist in the recipient's inbox - deleting the email in your account doesn't affect their copy.
Can you delete an Outlook email you sent?
Yes, you can try to delete / unsend an Outlook email you've sent, but there are important limitations and conditions to keep in mind.
Outlook offers a feature called Message Recall, which lets you retrieve a message sent in error. It's important to note that recalling an email is not the same as deleting it. Deleting removes your copy of the email from your account, while recalling attempts to remove the message from the recipient's inbox.
However, the recall feature isn't foolproof and has limitations:
- Recipient action. The recall will only work if the recipient has not yet opened the email. Once a message is opened, it cannot be recalled.
- Email accounts. Recalling is possible if both the sender and the recipient are using Microsoft Exchange or Office 365 accounts. It does not work for emails sent to external accounts like Gmail, Yahoo, or Hotmail.
- Outlook versions. The recall feature is only available on the Windows desktop version of Microsoft Outlook. It is not supported on Outlook for Mac and Outlook on the web.
In summary, while the Recall feature can be useful, its effectiveness depends on several factors, including the recipient's actions, the type of accounts involved, and the version of Outlook being used. For emails sent to external recipients or those using unsupported platforms, recall attempts will fail.
If you're unable to recall an email, consider following up with a clarification or enabling Delay delivery to give yourself extra time to review before sending.
Does deleting email in Outlook also remove it from server?
Whether a deleted message is also removed from server depends on what type of an email account you use and the stage of deletion. Here’s what you need to know:
IMAP accounts
If your account is set up using IMAP (commonly used for services like Gmail, Yahoo, or Outlook.com), then yes, deleting emails in Outlook also deletes them from the server.
IMAP syncs your email across all devices and the server. So, when you delete a message in Outlook, it's also removed from the server and any other devices where the account is synced.
However, the email typically first moves to the Deleted Items folder, both in Outlook and on the server, allowing you to recover it before permanent deletion.
POP accounts
With POP accounts (less common today), messages are not deleted from the server by default. POP downloads emails from the server to your device, often leaving the original email on the server unless configured otherwise.
You can adjust this behavior in Outlook settings by choosing whether to keep or delete copies of emails on the server.
Exchange accounts
For Exchange or Microsoft 365 accounts, deleting emails in Outlook removes them from the server.
These accounts use a two-way sync, meaning changes made in Outlook are reflected on the server and across all synced devices.
Like IMAP accounts, deleted emails are moved to the Deleted Items folder first, allowing for recovery before permanent deletion.
Key takeaways
- Deleting an email in Outlook doesn't remove it immediately – it first moves to the Deleted Items folder, where you can still recover it if needed.
- Whether others can see a deleted message depends on several factors, such as whether you attempted to recall a sent email or simply deleted it from your Sent Items folder.
- Whether deleting an Outlook email also removes it from the server depends on the type of account you're using (IMAP, POP, or Exchange).
Taking time to understand how email deletion works in Outlook helps you stay in control of your messages and keep your information secure.
 by
by
10 comments
I had emails on my work outlook account which seem to disappear. I'd sent one of them to a colleague who asked me to resend it after we'd looked at it on his machine the day before and it seemed to be missing. He said maybe i'd recalled it. I don't even know how to recall an email. We went to my desk and email to check to see if it was in my sent item's, it was not. As I was searching for all emails pertaining to the subject of the email in question, the system outlook system seemed freeze up then even the picture that I had on the screen from a previous email closed and I could not retrieve it 1 min. later. when the system unfroze. Now I can't find any reference or emails pertaining to that subject. Is it possible that someone with admin rights has deleted the emails from my account on the server. If so is there a way to restore the emails or tell that this has been done.
Hello Angelia,
If you’re using Microsoft 365 or an on-premises Exchange environment, your administrator has the ability to delete emails from the server, automatically through a rule or manually.
To investigate what might have happened to your missing message, try the following steps:
1. Search for the email in your Deleted Items and Recoverable Items folders. It might have been accidentally deleted but still recoverable.
2. If you have automatic archiving enabled on your computer, the email could have been moved to your archive file.
3. Check with your administrator whether any mailbox rules or retention policies could have removed the message, or if the admin manually deleted it.
Hi,
Question. I use simply free outlook account mainly via mobile. Now I have noticed that items in the recoverable folder are stored there for several months, until I deleted them. Outlook support keeps saying that it is 30 days or other person says 60. It is all very unclear. But I have experienced at time of manually emptying this folder, items kept from 4 months ago.
Personally I do not favour this recoverable folder (you cannot access it in the app) but if it's there, at least give reliable info.
Do you have more specifics?
Thank you
Hi Cornelis,
Please check out Step 2. Recoverable Items folder in this tutorial. Also, you may find useful info in the article How to permanently delete emails from Outlook.
hi if I sent someone with files attached to it in outlook, then deleted from my sent can they still see it like is it only gone for me or them too?
Hi!
Your recipients can still see your files and your message. Deleting an email from your Sent Items folder only removes your copy of the message, it does not affect the recipient's copy in any way. If you want to remove the message from the recipient's mailbox, you can try recalling the email.
If I sent an email with attachments but everyone says they didn't get it ...so I deleted it from my sent and just sent the files individually/...will the ones deleted still go through?
Hello Didi,
Deleting the email from your Sent folder won’t affect its delivery if it was already sent. If the recipients didn’t receive it, the issue could be due to various reasons - attachment size limits, spam filters, or server delays. Additionally, some email servers are configured to remove attachments with certain file types, such as .exe or .zip, for security reasons. You might want to check with your email provider or ask recipients to check their spam/junk folders.
If I delete something to recovered items from one device e.g phone can I definitely recover it from another laptop?
Does the message have to be seen/viewed for it to be recovered?
Also if I can't find an email in recovered items that was deleted recently, why might that be please? Thanks
Hi! Yes, if you delete an item in Outlook on one device (e.g., your phone), you can recover it from another device (e.g., your laptop). The deleted items are stored on the server, so they are accessible from any device where you access your Outlook account.
The message does not need to be seen or viewed for it to be recovered. As long as it is in the Deleted Items or Recoverable Items folder, you can recover it.
If you can't find an email in the Recoverable Items folder that was deleted recently, there could be several reasons:
1. The email might have been permanently deleted if it exceeded the retention period for deleted items (usually 14 to 30 days, depending on your settings).
2. The email might be in a different folder, such as Junk Email or another custom folder.
3. There might be a delay in synchronization between devices, so the email might not appear immediately.